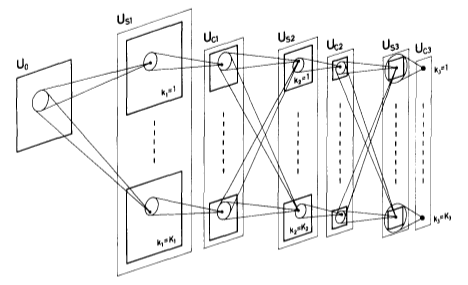
A hierarchical multi-layered neural network, proposed by Kunihiko Fukushima in 1982.
It has been used for handwritten character recognition and other pattern recognition tasks.
Since backpropagation had not yet been applied for training neural nets at the time, it was limited by the lack of a training algorithm.
source
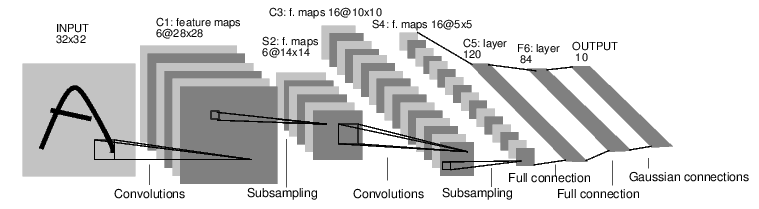
A pioneering digit classification neural network by LeCun et. al.
It was applied by several banks to recognise hand-written numbers on checks.
The network was composed of three types layers: convolution, pooling and non-linearity, and was trained using the backpropagation algorithm.
source
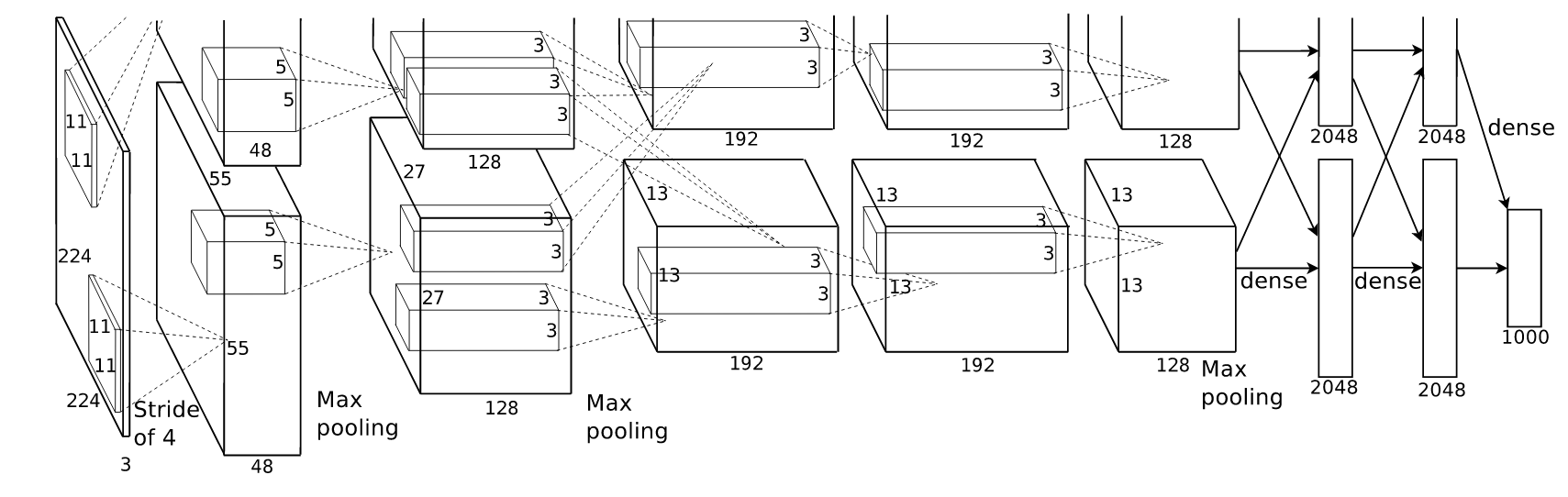 A convolutional neural network, which competed in the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge in 2012 and achieved a top-5 error of 15.3%, more than 10.8% ahead of the runner up.
AlexNet was designed by Alex Krizhevsky, Geoffrey Hinton, and Ilya Sutskever.
The network consisted of five convolutional layers, some of which were followed by max-pooling layers, and three fully-connected layers with a final 1000-way softmax.
All the convolutional and fully connected layers were followed by the ReLU nonlinearity.
A convolutional neural network, which competed in the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge in 2012 and achieved a top-5 error of 15.3%, more than 10.8% ahead of the runner up.
AlexNet was designed by Alex Krizhevsky, Geoffrey Hinton, and Ilya Sutskever.
The network consisted of five convolutional layers, some of which were followed by max-pooling layers, and three fully-connected layers with a final 1000-way softmax.
All the convolutional and fully connected layers were followed by the ReLU nonlinearity.
source
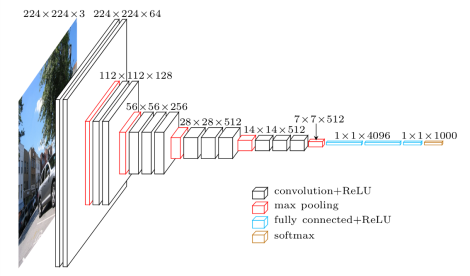
A 19 layer convolutional neural network from VGG group, Oxford, that was simpler and deeper than AlexNet. All large-sized filters in AlexNet were replaced by cascades of 3x3 filters (with nonlinearity in between). Max pooling was placed after two or three convolutions and after each pooling the number of filters was always doubled. source
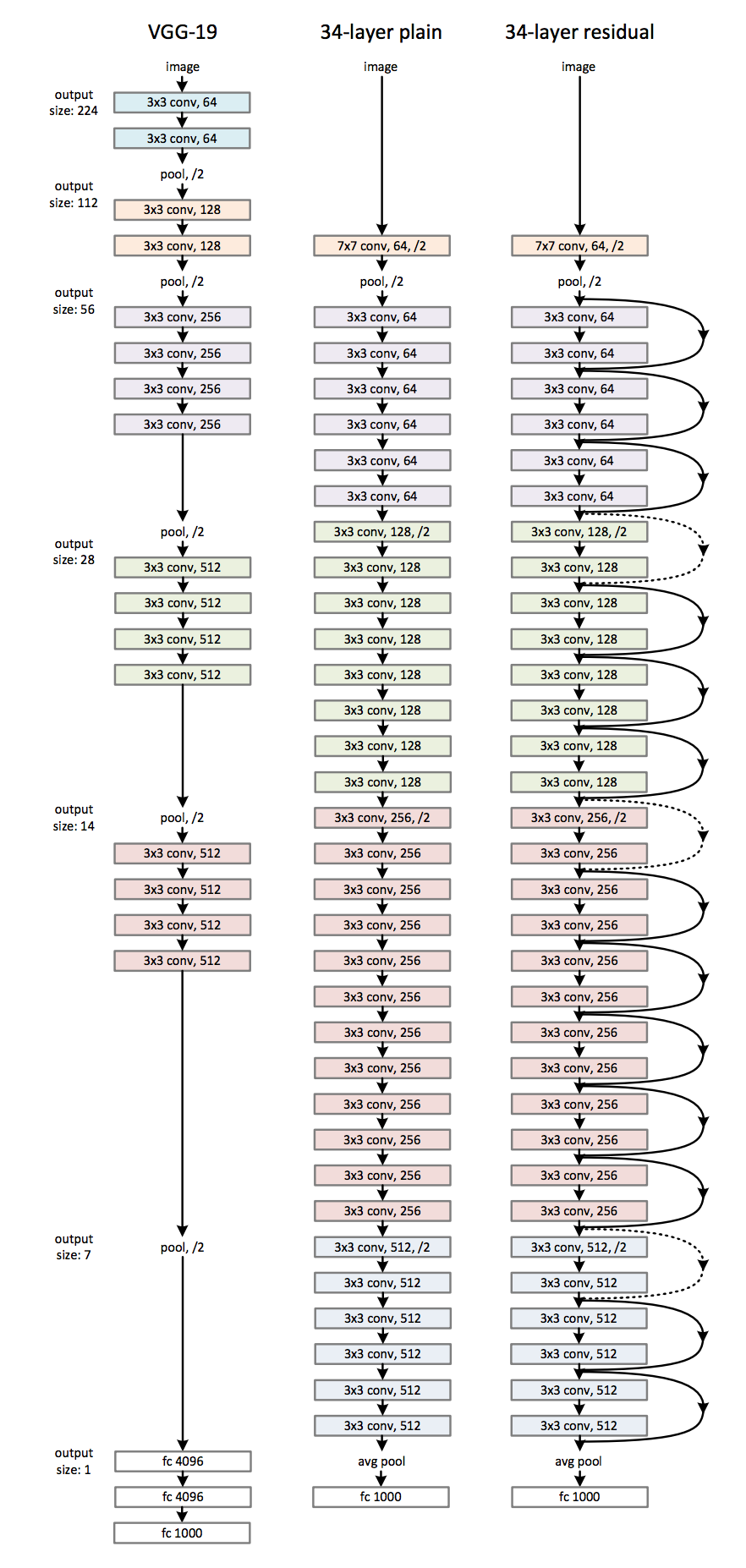
Developed by Microsoft Research, ResNet won first place in ILSVRC 2015 image classification using a 152-layer network -- 8 times deeper than the VGG. The basic element in this architecture is the residual block, which contains two paths between the input and the output, one of them being direct. This forces the network to learn the features on top of already available input, and facilitates the optimization process.
